Monopolistic Competition
In a monopolistic competitive market, numerous suppliers are offering distinctive but similar products. There is a lot of information for the consumer to absorb and evaluate to make the best decisions. Advertising drives up costs, but it's necessary to stand out.
Examples: apartments, books, canned water clothing monopolistic competition is a blend of monopoly and perfect competition. Monopolistic competition is easily obtained in the real world. Monopolistic competition is a market situation in which a large number of firms produce differentiated products yet closed substitutes and there is free entry and exit of farms.
In general, the market structure with mixed features of monopoly and perfect competition is Tom days monopolistic competition. This market structure was developed by E Chamberlain and John Robinson.
The main features of monopolistic competitions are
Product differentiation/Each business creates things that are comparable but different.
A large number of sellers/ the existence of numerous businesses
Free entry and exit/ Freedom of entry and departure of firms/industry
Strategy strategies to make their products unique
Heavy investment in advertisements
A lack of price competition
Perfect market and technological knowledge
Nature of Demand Curve of Monopolistic Competition
A firm with some market power has a downward-sloping demand curve, which is a sign of monopolistic competition. Since each company develops a unique product, market power is derived from product differentiation. Since there are numerous close alternatives for each thing, market power is constrained. If prices are raised too much, customers will switch to rivals' goods.
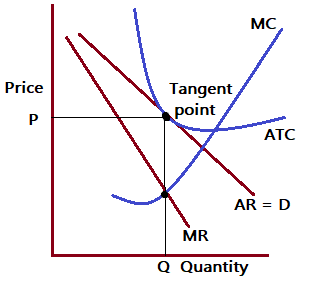
The demand curve or average revenue in monopolistic competition has characteristics that fall between those of perfect competition and monopoly, or it is of a reasonably elastic nature.Short-run Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition
Zero Profit in the Long run
Up until profits are equal to zero and total revenues are equal to total costs, new businesses can enter the market. At the ideal long-term quantity, the demand curve is therefore tangent to the average cost curve. Some businesses leave the market if there is a loss, whereas the surviving businesses eventually turn a profit.