Let's respond to the following before talking about macroeconomics:
• Which factors determine how many goods and services a country can produce?
• What determines the number of jobs available in an economy?
• What determines a country’s standard of living?
• What factors cause the economy to speed up or slow down?
• What causes organizations to hire or fire more labor on a national scale?
• What causes the economy to grow over the long term?
• What the state of the nation’s economic health is, based on improvement in the standard of living, low unemployment, and low inflation(Inflation is the decline of purchasing power of a given currency over time)?
Objectives of Macroeconomics
- To explain principles, problems, and policies related to full employment and growth of resources.
- Macroeconomics seeks to explain how economic activity helps countries achieve their goals by offering a theory of the economy's components and the economy as a whole.
- The interactions between various sectors of an economy must also be covered in the study.
- Explaining changes in overall activity or output over time, including changes in pricing, income distribution (including tax revenue), and changing levels or rates of production or consumption, is the focus of macroeconomics.
- It also explores the relationships between these elements and other elements including population growth rates, technological advancements, and governmental regulations.
Importance of Macroeconomics
To understand the
working of the economy: Macroeconomics studies the economy in its aggregate form. It studies how macroeconomic variables are determined, how they are interrelated, and
how the change in one macroeconomic variable influences other variables and
aspects of the whole economy. Hence, it helps in knowing the functioning of the
economy.
Helps in devising
suitable policies: The problem of inflation, unemployment, and economic growth are the
major reasons for headaches for both developed and underdeveloped countries.
These problems carry so much weight that keeping them under a certain level can
keep a government stable and failure to address such problems can collapse the
whole government. The knowledge of the working of the economy and the
interrelationship between economic variables helps the government to devise
appropriate policies to solve these serious problems.
Helps in
comparison: The
macroeconomic indicators like GDP, Inflation, and Unemployment percentage act as
the standard against which relative developments of countries over time can be
compared. A country's relative development in the present can be known compared
to the past.
To know the
effectiveness of policies: Macroeconomics gives various tools and techniques to know the
effectiveness of using various policies under given situations. Basically, the
IS-LM model helps to know the policy effectiveness of using various policies.
It also sheds light on the fact that sometimes a single policy cannot help to
achieve the stated objectives and hence the judicious mix of both policies
is necessary. Moreover, it helps to throw light on the fact that microeconomic
laws do not apply under macro situations.
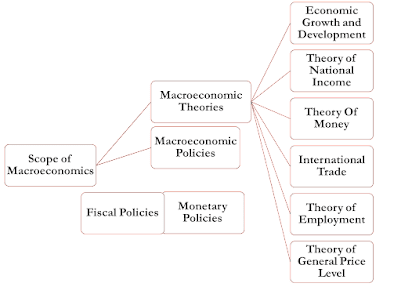
Scope of Macroeconomics
The scope of macroeconomics has been explained under Macroeconomic theories:-
👉Economic Growth and Development: As discussed in the macroeconomics discipline, the state of a nation's economy can be assessed in terms of the real per capita income. It explains various issues relating to privatization, liberalization, globalization, balanced development, poverty, inequality, etc.
👉Theory of National Income:-
Macroeconomics studies the concept of national income, its different elements, methods of its measurement, and social accounting.
👉Theory of Money: -
Changes in the demand and supply of money affect the level of employment. Therefore, under macroeconomics functions of money and theories relating to money are studied.
👉Theory of International Trade:-
It also studies principles determining trade among different countries. Tariff protection and free-trade policies fall under foreign trade.
👉Theory of Employment:-
It studies the problems of employment and unemployment. Different factors determine employment. They are effective demand, aggregate demand, aggregate supply, total consumption savings, total investment, etc.
👉Theory of General Price Level:-
A continuous rise in the price level is called inflation. It distorts production. It increases inequalities in the distribution of income and wealth. The common man is injured by inflation. Deflation is the opposite of inflation. The general price level falls continuously. Output and employment levels fall. Macroeconomics provides an explanation for the occurrence of inflation and deflation.
👉 Theory of distribution:-
There are macroeconomic theories of distribution. These theories try to explain how the national output is distributed among the factors of production.
👉Theory of Business Fluctuations:-
It also deals with the fluctuations in the level of employment, total expenditure, income, output, and general price level.
👉Macroeconomic Policies:-
For the welfare and development of the country, the government and central bank work together to decide on macroeconomic policies. Macroeconomics studies two types of macroeconomic policies. They are Monetary policies and fiscal policies.
Fiscal Policy: Fiscal policy is a type of budgetary choice that aims to address the income over-expenditure deficit. Fiscal policy deals with government revenue, government expenditure, government borrowing, and government budget.
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence therall economic activity and achieve certain objectives. It involves decisions related to government revenue and expenditure to stabilize the economy and promote economic growth.
Types of Fiscal Policy:
Expansionary Fiscal Policy: This involves increasing government spending or reducing taxes to stimulate economic activity during times of recession or low growth.
Contractionary Fiscal Policy: This entails reducing government spending or increasing taxes to slow down economic activity and control inflation during periods of high growth.
Objectives of Fiscal Policy:
The main objectives of fiscal policy are:
Economic Stability: Fiscal policy aims to stabilize the economy by managing aggregate demand and maintaining price stability.
Economic Growth: Fiscal policy can be used to stimulate economic growth through increased government spending on infrastructure and investment.
Redistribution of Income: Fiscal policy can help reduce income inequality by implementing progressive tax systems and social welfare programs.
Full Employment: Fiscal policy can be employed to achieve full employment by increasing government spending and stimulating job creation.
Instruments of Fiscal Policy:
The key instruments of fiscal policy include:
Government Spending: Governments can increase spending on infrastructure, education, healthcare, and other sectors to stimulate economic activity.
Taxation: Governments can adjust tax rates and policies to influence disposable income and consumption patterns.
Transfer Payments: Governments can provide social welfare benefits and subsidies to individuals and businesses to support specific economic sectors.
Monetary Policy:
Monetary policy refers to the management of the money supply, interest rates, and credit conditions by a central bank to influence economic activity and stabilize the economy. Monetary Policy: Monetary policy deals with money supply, interest rate, foreign exchange rate, banking system, credit creation and control, price stability, and many other aggregate variables related to money and banking of an economy. The central bank and the government work together to create monetary policy. By controlling the various interest rates, these policies aim to sustain the nation's economic growth and stability.
Types of Monetary Policy:
Expansionary Monetary Policy: This involves increasing the money supply, lowering interest rates, and providing easy credit to stimulate economic growth.
Contractionary Monetary Policy: This entails reducing the money supply, increasing interest rates, and tightening credit conditions to control inflation and cool down an overheating economy.
Objectives of Monetary Policy:
The main objectives of monetary policy are:
Price Stability: Monetary policy aims to maintain stable prices and control inflation within a target range.
Full Employment: Monetary policy seeks to achieve maximum employment levels by supporting a conducive economic environment.
Economic Growth: Monetary policy can stimulate economic growth by providing favorable borrowing conditions and supporting investment.
Instruments of Monetary Policy:
The key instruments of monetary policy include:
Open Market Operations: Central banks buy or sell government securities to influence the money supply and interest rates.
Reserve Requirements: Central banks set the minimum reserve ratio that commercial banks must hold, impacting their lending capacity.
Interest Rates: Central banks adjust the benchmark interest rates to influence borrowing costs and credit availability.
There is another policy in macroeconomics, called income policy. This policy directly controls prices and wages.
Types of Macroeconomics
Interdependence Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Dependence of Microeconomics on Macroeconomics
Macroeconomic Fundamental
Macroeconomic Public Goals
The macroeconomic public goals are the objectives that a government seeks to achieve through its economic policies. These goals generally include:
Price stability - maintaining a low and stable rate of inflation.
Full employment - achieving maximum sustainable employment.
Economic growth - increasing the long-term capacity of the economy to produce goods and services.
Balance of payments stability - ensuring a sustainable balance of payments position, including a stable exchange rate.
Distributional equity - reducing income and wealth inequality.
Stable financial system - maintaining stability in the financial system and avoiding financial crises.
It is noted that these goals may sometimes conflict with each other, and trade-offs may need to be made.
Macroeconomic Problems
Limitations of Macro Economics
👉The danger of excessive thinking in terms of aggregates: There is a danger of executive thinking in terms of aggregates that are not homogeneous. For example, 2 apples +3apples=5 apples mean full aggregate, similarly 2 apples +3 oranges are meaningful to some extent.
👉Aggregate tendency may not affect all sectors equally: For example, the general increase in price affects different sections of the community or the different sectors of the economy differently. The increase in the general level of price benefits the producers but hurts the consumers.
👉Indicates no change has occurred: The study of aggregates makes us believe that no change has occurred even if there is a change. It indicates that there is no need for a new policy. For example, a 5 percent fall in agricultural prices and a 5 percent rise in industrial prices do not affect the price level.
👉Difficulty in the measurement of aggregates: There are at times, difficulties in the measurement of aggregates. It is difficult to measure the big aggregates. This problem has now been more or less erased by the use of calculators and things that are not homogeneous.
👉 The fallacy of composition: The aggregate economic behavior is the sum of individual behavior. This is called fallacies of composition. What is true in the case of an individual may not be true in the case of the economy as a whole. For example, individual saving is a virtue, whereas public saving is a vice.
👉It ignores the contribution of Individual Units: Macroeconomic analysis only throws light on the aggregates' functioning. However, in real life, the economic activities and decision taken by individual units on a private- level have their effects on the economy as a whole.
👉Limited Application: Another limitation of macroeconomics is that most of the models relating to it have only theoretical significance. They have very little use in practical life.